nTRACK Strives to Track Stem Cells in Real-Time
There is a need of tools to evaluate and predict the safety and success of cell-based treatments in earlier stages. The current lack of methods providing real-time tracking of transplanted cells and knowledge on their early biodistribution and viability is one of the major weakness of the available cell-based treatments. These treatments can sometime be ineffective due to poor or unspecific targeting or lead to tumor developments. Therefore, to fulfil this need, nTRACK develops a safe and highly sensitive multimodal nanoimaging agent enabling non-invasive and quantitative stem cell tracking in the entire body.
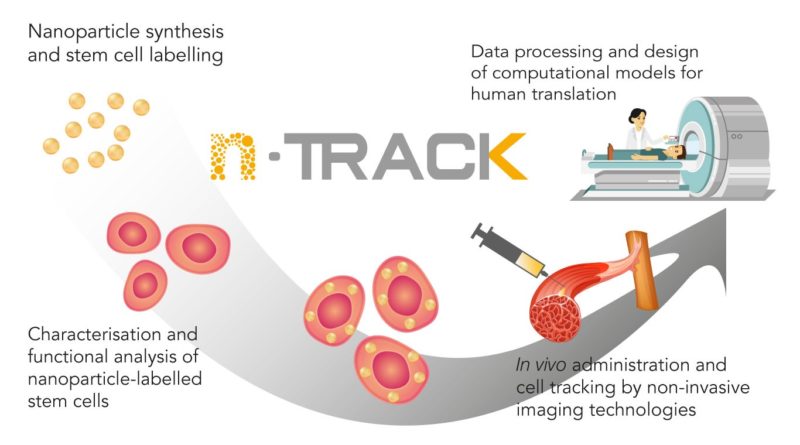
The principle of nTRACK is to insert iron oxide nanoparticles with a gold shell in stem cells and inject those labelled stem cells in the body in order to foster muscle regeneration. The nanoparticles allow a precise tracking of the stem cells up to the injured organ of the body. This bimodal technology tracks cells with Computer Tomography (CT) thanks to the gold shell and with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) sensitive to the presence of magnetic iron oxide.
The project focuses on four main domains of activities. First, the production of the nanoparticles by using manufacturing methods that complies Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), mainly by a German company, MJR PharmJet. The particles are loaded into the stem cells provided by Pluristem, an Israeli company. Two strategies have been developed due to differences in development velocities. One where the nanoparticles are only made of gold fulfilling the GMP standards but not compatible with MRI. The second one consists of the iron oxide nanoparticle with gold shell by the Bar-Ilan University (Israel), but their manufacturing method does not fulfil the GMP requirements, yet.
Second, the proof of concept aims to show that the contrasting agent is working correctly with the different imaging techniques such as CT and MRI. Depending on the strategy, stem cells with different types of nanoparticles are being used during in-vivo studies. BIOEMTECH, a Greek company develops an AI algorithm capable of counting the stem cells in the targeted body part and identify migration patterns.
Third, Leitat is conducting in vitro and in vivo exploratory toxicological assays to provide insight for the preclinical safety regulatory studies, that will be conducted by Vivotecnia. The studies in rats will allow selecting the most relevant administration method and animal model and adequate follow-up periods. From the data analyzed up to now, no relevant in vivo toxic effects have been observed. The VHIR (Vall d’Hebron Institute of Research, Spain) and Leitat are carrying out the generation of small and large animal muscle lesion models and the analysis of the medical images. The VHIR has also developed a virtual model for muscle regeneration prediction algorithms based on the in vivo studies. Furthermore, they have recently submitted a publication where they have been able to predict the muscle regeneration of a small animal with an unusual radiological technique, such as TAC, which is a huge achievement.
Lastly, the regulatory part prepares the market entry of the technology in direct contact with regulatory authorities. Discussions with the European Medical Agency (EMA) Innovation Task Force resulted in recommendations on the categorization of the nTRACK technology. Further work by Asphalion, a Spanish Consultancy on Scientific and Regulatory Affairs and RIVM, the Dutch National Institute for Public Health and the Environment, is currently being carried out with National Competent Authorities to seek scientific advice on the studies planned.
Read the full newsletter here.